
Stabilisation dynamique interépineuse
Contrairement aux spondylodèses, le concept de base est de stabiliser la colonne sans la bloquer. Tous les dispositifs vont limiter l'excès de lordose lombaire et réaliser une ouverture des foramens. Certains dispositifs vont aussi limiter l'excès de cyphose, mais se rapprochent plus dès lors d'une spondylodèse.
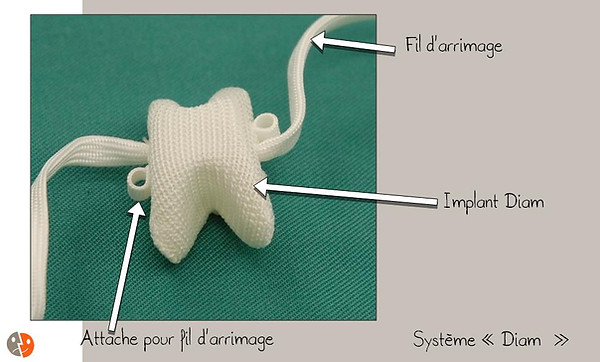
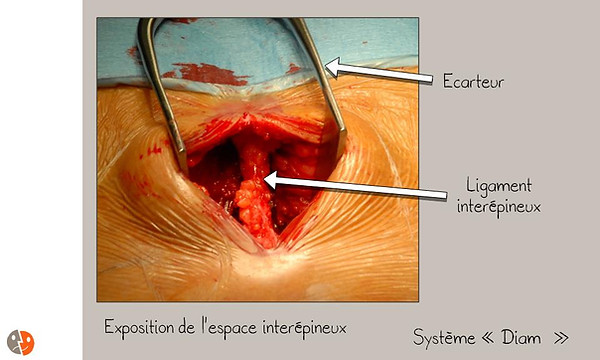
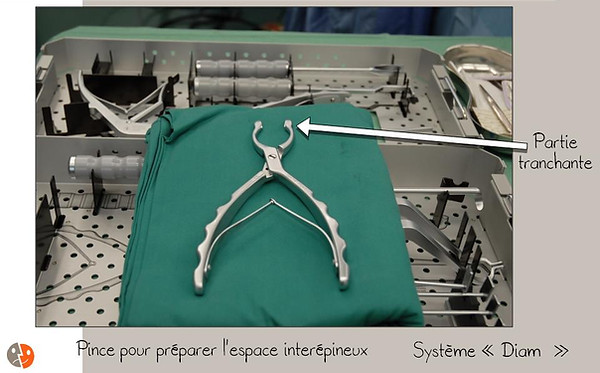
Diam

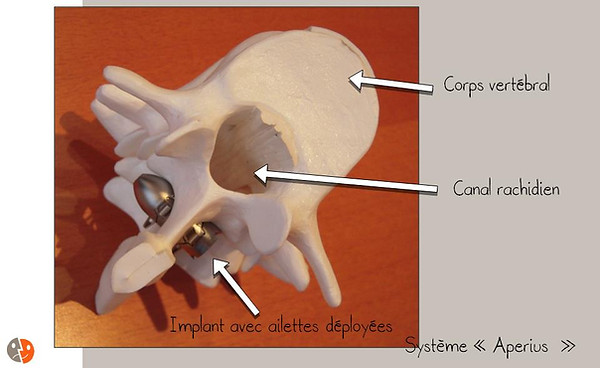
Aperius
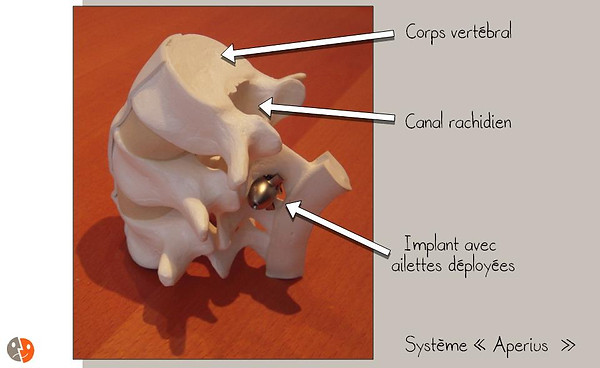

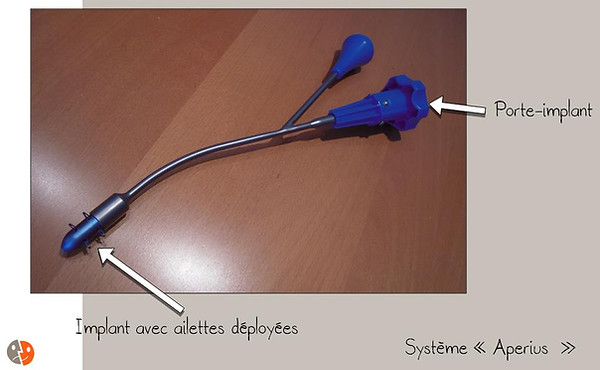
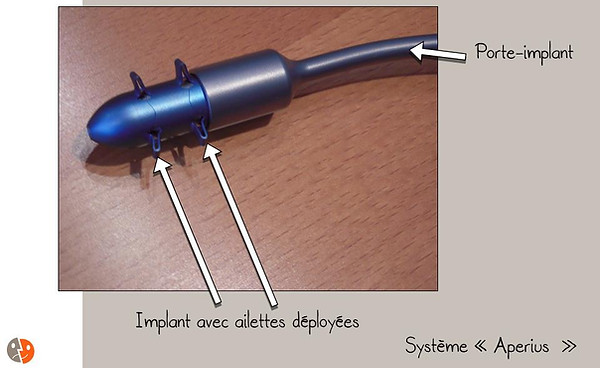



Complications:
-
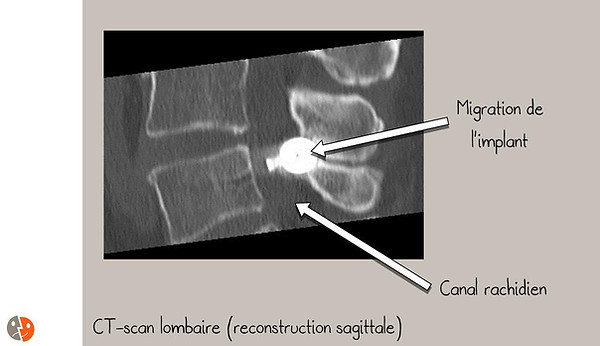
Migration intracanalaire de l'implant. Si une hémilaminectomie large a préalablement été pratiquée, il y a un risque faible de migration de l'implant dans le canal rachidien. Cela entraîne une compression du sac dural et des racines et nécessite en règle générale une réintervention pour enlever l'implant et le substituer par un autre avec des appuis différents comme le Backjack.
-
Fistule de LCR. Si le ligament jaune est très fin et la graisse épidurale peu importante, une ailette de l'Aperius pourrait éroder le ligament jaune, puis la duremère et l'arachnoïde et entrainer une fistule. Cela n'est guère possible qu'en L5-S1.
-
Fracture de l'apophyse épineuse. La pression exercée sur l'apophyse épineuse est importante et pourrait entrainer une fracture de celle-ci, particulièrement en cas d'ostéoporose. L'Aperius s'appuyant sur la base de l'épineuse et proche du départ des lames, cela est très rare car l'os est heureusement plus résistant à cet endroit.

Bacjac



